Let’s face it, some of the language we use to describe principles of learning are loaded terms, and at the same time, we still need to know them. Use this step-by-step guide to help you breakdown operant learning scenarios with ease!
- WHO is the behaver? Whose behavior are we interested in?
- Is the BEHAVIOR of interest INCREASING (reinforcement) or DECREASING (punishment)?
- After the behavior occurs, is a STIMULUS ADDED or REMOVED (i.e., taken away)? If something is added after the behavior, let’s say a shock, then that’s positive. If something is being taken away or removed after the behavior, like a headache or a gaming system, that’s negative. Remember, things don’t have to sound good or bad to be positive or negative, it’s not about the quality -- it’s about whether something is being ADDED or REMOVED.
- Put it all together! Use the table as a visual to help guide you.
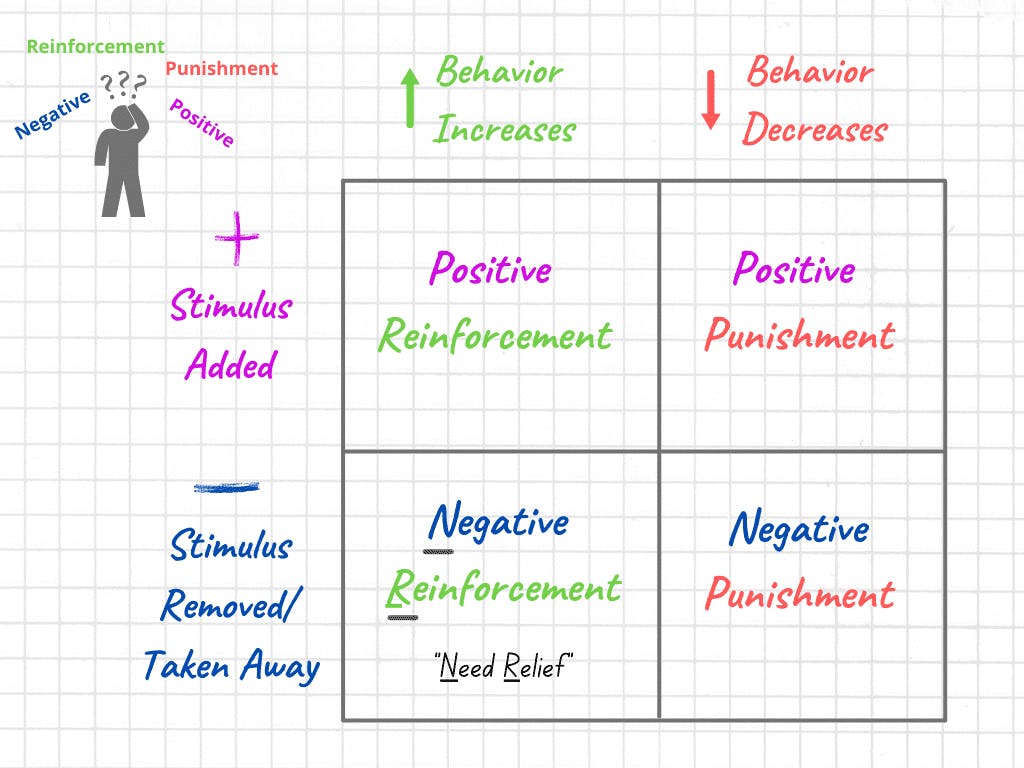
Let’s try a scenario!
Every morning, Mara’s alarm clock starts blaring at 5am so she can get ready for her shift at the hospital. Her partner, who doesn’t need to wake up at 5am puts their pillow over their head so they don’t have to hear this awful sound. Without fail, Mara hits the snooze button so she can get some peace and quiet and repeats this every 10 minutes until she finally gets up at 5:30am. Mara’s behavior of hitting the snooze button is under the control of what type of principle of learning?
- Whose behavior are we interested in? Mara’s behavior of hitting the snooze button.
- Is the behavior of interest increasing or decreasing? Mara hitting the snooze button increases – this is reinforcement.
- After the behavior occurs, is a stimulus being added or removed? Alarm clock sound is being removed – this is negative.
Mara hitting the snooze button is under the control of negative reinforcement.
TIP:
Negative reinforcement is often about engaging in a behavior to escape an aversive stimulus. Taking medication to get rid of a headache. Running away from a crowded festival to reduce feelings of anxiety. A good way to remember this is:
Negative Reinforcement = Needs Relief


